ADB Instructions
Update time:2017-12-29 Views:1673
Foreword
adb, full name Android Debug Bridge, Android command line debugging tools, it has a variety of functions, such as tracking system logs, upload and download files, install applications.
Prepare
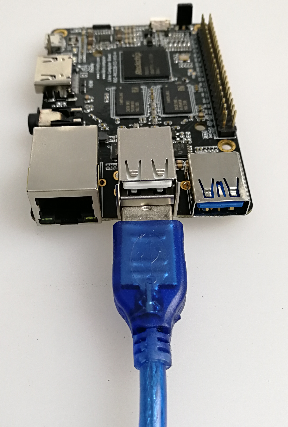
Connect the device with the data cable (the underlying USB interface) and the host as shown.
In the development board , enter: Settings-> USB, check the "Connect to PC" option.
ADB Install for Windows
First of all, install driver refer to the installation of RK USB driver section.
donwload adb.zip from the website http://adbshell.com/download/download-adb-for-windows.html,then unzip it in path C:\adb to call it conveniently。
Open a command line window and input:
cd C:\adb adb shell
If everything is normal, you can enter the adb shell, and run some commands.
ADB Install for Ubuntu
Install adb tool:
sudo apt-get install android-tools-adb
Add device ID:
mkdir -p ~/.android vi ~/.android/adb_usb.ini # add the following line: 0x2207
Add udev rules:
sudo vi /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
# add the following line:
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="2207", MODE="0666"
Reseat the data cable Type-C or run the following command to make the udev rule take effect:
sudo udevadm control --reload-rules sudo udevadm trigger
Restart adb server
sudo adb kill-server adb start-server
Commonly Used ADB Command
Connection management
List all connected devices and their serial numbers
adb devices
If there are multiple connected devices, you need to use the serial number to distinguish:
export ANDROID_SERIAL=<device serial number> adb shell ls
Adb can be connected via the internet:
# Allow adbd restart on the device side and listen on TCP port 5555 adb tcpip 5555 # Type-C connection can be disconnected at this time # Connect to the device remotely. The IP address of the device is 192.168.1.100 adb connect 192.168.1.100:5555 # Disconnect adb disconnect 192.168.1.100:5555
Debug
Get system log adb logcat
usage
adb logcat [option] [Application label]
example
# View all logs adb logcat # View only part of the log adb logcat -s WifiStateMachine StateMachine
run: adb shell
Get detailed operating information: adb bugreport
adb bugreport is used for error reporting, which contains a wealth of useful information.
example
adb bugreport # Save to local, make it easy to use editor view adb bugreport >bugreport.txt
Application Management
use adb install to install apk
usage:
adb install [option] example.apk
Options include:
-l forward-lock -r Reinstall the application to retain the original data -s Install to SD card instead of internal storage
example:
# install facebook.apk adb install facebook.apk # upgrade twitter.apk adb install -r twitter.apk
If install sucessfully,The tool will return a success message "Success"; if it fails, it will generally be the following
INSTALL_FAILED_ALREADY_EXISTS: Means that you need to use the-r parameter to reinstall.
INSTALL_FAILED_SIGNATURE_ERROR: Means that application signature is inconsistent, and it may be due to the different version of the signature and debug version. If you confirm the APK file signature is normal, you can use the adb uninstall command to uninstall the old application, and then install.
INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE: Means that not enough storage space and need to check equipment storage.
Uninstall apk: adb uninstall
usage:
adb uninstall apk_name
example:
adb uninstall com.android.chrome
The name of the application package can be listed with the following command:
adb shell pm list packages -f
The result is:
... package:/system/app/Bluetooth.apk=com.android.bluetooth ...
The former is the apk file, the latter is the corresponding package name.
Command line help information: adb help
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.31
-a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s <specific device> - directs command to the device or emulator with the given
serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL
environment variable.
-p <product name or path> - simple product name like 'sooner', or
a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT
environment variable is used, which must
be an absolute path.
-H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
-P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
devices [-l] - list all connected devices
('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this command with no additional arguments
will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push [-p] <local> <remote>
- copy file/dir to device
('-p' to display the transfer progress)
adb pull [-p] [-a] <remote> [<local>]
- copy file/dir from device
('-p' to display the transfer progress)
('-a' means copy timestamp and mode)
adb sync [ <directory> ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
(see 'adb help all')
adb shell - run remote shell interactively
adb shell <command> - run remote shell command
adb emu <command> - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - View device log
adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
the format is a list of lines with the following format:
<serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n"
adb forward <local> <remote> - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
dev:<character device name>
jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote>
- same as 'adb forward <local> <remote>' but fails
if <local> is already forwarded
adb forward --remove <local> - remove a specific forward socket connection
adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-l] [-r] [-d] [-s] [--algo <algorithm name> --key <hex-encoded key> --iv <hex-encoded iv>] <file>
- push this package file to the device and install it
('-l' means forward-lock the app)
('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data)
('-d' means allow version code downgrade)
('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage)
('--algo', '--key', and '--iv' mean the file is encrypted already)
adb uninstall [-k] <package> - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport - return all information from the device
that should be included in a bug report.
adb backup [-f <file>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] [<packages...>]
- write an archive of the device's data to <file>.
If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
(-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
in the archive; the default is noapk.)
(-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
(aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
is noobb.)
(-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
(-all means to back up all installed applications)
(-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
system applications; the default is to include system apps)
(<packages...> is the list of applications to be backed up. If
the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
command line will be included even if -nosystem would
ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
adb restore <file> - restore device contents from the <file> backup archive
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
scripting:
adb wait-for-device - block until device is online
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints: <serial-number>
adb get-devpath - prints: <device-path>
adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device
adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program
adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip <port> - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port
networking:
adb ppp <tty> [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
<tty> refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb sync notes: adb sync [ <directory> ]
<localdir> can be interpreted in several ways:
- If <directory> is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition
is updated.
environmental variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.